Home » Financial Math
Category Archives: Financial Math
Two-Way Table Data Probability problems
Two Way Table Data Conditional Probability example problem
When insurance companies establish policies for overing screening tests for diseases, one important factor is the value of the test predicting the disease. For example, for a certain type of disease, insurance companies may only cover the test costs if the test improves the prediction of having the disease by 80%. To help decide coverage policy for a new test, use the following data to help decide whether the test should be covered.
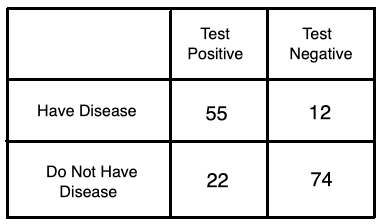
a) Find P(A) = P(Having the disease among everyone)
b) Find P(B) = P(Testing positive for everyone)
c) Find P(A and B) = P(Having the disease and testing positive)
d) Find P(A | B) = P(Having the disease given tested positive)
e) Should the test be covered? What is your conclusion? Justify your answer using the conditional probabilities above.
Solution to this Calculus Two Way Table Data Conditional Probability practice problem is given in the video below!
Compound Interest problems
Compound Interest example problem
Suppose you make a deposit of $8,000 in the bank account that earns you 5.5% interest. Assuming that you are not withdrawing any funds, find the amount, in dollars, that will be in your bank account 1 year from the date of your initial deposit if
a) Interest is compounded daily
b) Interest is compounded monthly
c) Interest is compounded quarterly
d) Interest is compounded continuously
Solution to this Compound Interest practice problem is given in the video below!
TRY IT YOURSELF example question
On January 1, 2021 you borrow a $15,000 loan from the bank with a 7.5% accrued interest. If you do not plan on making any payments during the loan period, find the total balance of your loan, in dollars, that you will owe to the bank on January 1, 2022 for
a) Daily compounded interest
b) Weekly compounded interest
c) Monthly compounded interest
d) Quarterly compounded interest
e) Semi-annually compounded interest
f) Continuously compounded interest
Business Calculus Optimization problems
Demand Revenue Optimization example problem
A store has been selling 200 DVD burners a week at $350 each. A market survey indicates that for each $10 rebate offered to buyers, the number of units sold will increase by 20 a week. Find the demand function and the revenue function. How large a rebate should the store offer to maximize its revenue?
Solution to this Business Calculus Optimization practice problem is given in the video below!
Continuous Distributions probability problems – SOA Exam P CAS Exam 1
Continuous Probability Density Function example question
The number of days that elapse between the beginning of a calendar year and the moment a high-risk driver is involved in an accident is considered to be a random variable with pdf ![]() . An insurance company expects that 30% of high-risk drivers will be involved in an accident during the first 50 days of a calendar year. What portion of high-risk drivers are expected to be involved in an accident during the first 80 days of a calendar year?
. An insurance company expects that 30% of high-risk drivers will be involved in an accident during the first 50 days of a calendar year. What portion of high-risk drivers are expected to be involved in an accident during the first 80 days of a calendar year?
Solution to this Society of Actuaries Exam P practice problem is given in the video below!
Discrete Distributions probability problems – SOA Exam P CAS Exam 1
Binomial Distribution Bayes Rule example question
A hospital receives ![]() of its flu vaccine shipments from Company X and the remainder of its shipments from other companies. Each shipment contains a very large number of vaccine vials. For Company X’s shipments, 10% of the vials are ineffective. For every other company, 2% of the vials are ineffective. The hospital tests 30 randomly selected vials from a shipment and finds that one vial is ineffective. What is the probability that this shipment came from Company X?
of its flu vaccine shipments from Company X and the remainder of its shipments from other companies. Each shipment contains a very large number of vaccine vials. For Company X’s shipments, 10% of the vials are ineffective. For every other company, 2% of the vials are ineffective. The hospital tests 30 randomly selected vials from a shipment and finds that one vial is ineffective. What is the probability that this shipment came from Company X?
Solution to this Society of Actuaries Exam P practice problem is given in the video below!
Binomial Distribution example problem
A company prices its hurricane insurance using the following assumptions:
(i) In any calendar year, there can be at most one hurricane
(ii) In any calendar year, the probability of a hurricane is 0.05
(iii) The number of hurricanes in any calendar year is independent of the number of hurricanes in any other calendar year.
Using the company’s assumptions, calculate the probability that there are fewer than 3 hurricanes in a 20-year period.
Solution to this Society of Actuaries Exam P practice problem is given in the video below!
Binomial Distribution Hard example
A company establishes a fund of 120 from which it wants to pay an amount, C, to any of its 20 employees who achieve a high performance level during the coming year. Each employee has a 2% chance of achieving a high performance level during the coming year, independent of any other employee. Determine the maximum value of C for which the probability is less than 1% that the fund will be inadequate to cover all payments for high performance.
Solution to this Society of Actuaries Exam P practice problem is given in the video below!
Binomial Distribution Multiple Random Variables example question
A study is being conducted in which the health of two independent groups of ten policyholders is being monitored over a one-year period of time. Individual participants in the study group drop out before the end of the study with probability 0.2 (independently of the other participants). What is the probability that at least 9 participants complete the study in one of the two groups, but not in both groups?
Solution to this Society of Actuaries Exam P practice problem is given in the video below!
Poisson Distribution example problem
An actuary has discovered that policyholders are three times as likely to file two claims as to file four claims. If the number of claims filed has a Poisson distribution, what is the variance of the number of claims filed?
Solution to this Society of Actuaries Exam P practice problem is given in the video below!
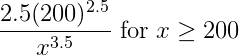
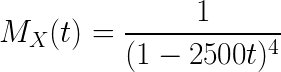
Recent Comments